Ecosystem: Meaning, Structure, Components and Functions
The simplest definition and meaning of the Ecosystem is as follows: It is a set of living creatures that live within an environment and interact with each other within that environment.

The community of living organisms of the Ecosystem is known as biocenosis, and the environment where they live is known as the biotope. A lake, for example, is the biotope and all the fish, crabs, and insects living in it are biocenosis. And if you wonder how many ecosystems there are in the world – know that they are found everywhere, in the forest, on the field, in the lake, etc. Similarly, ecosystems can be of any size, from a small pond to a large forest.
Table of Contents
- 1 What Is the Meaning of Ecosystem?
- 1.1 What Is a Terrestrial Ecosystem?
- 1.2 What Is a Forest Ecosystem?
- 1.3 What Is a Grassland Ecosystem?
- 1.4 What Is a Tundra Ecosystem?
- 1.5 What Is a Desert Ecosystem?
- 1.6 What Is a Mountain Ecosystem?
- 1.7 What Is a Savanna Ecosystem?
- 1.8 What Is an Aquatic Ecosystem?
- 1.9 What Is a Freshwater Ecosystem?
- 1.10 What Is a Marine Ecosystem?
- 2 What Is a Community in An Ecosystem?
- 3 What Are the Structural Components of The Ecosystem?
- 4 Functional Components of The Ecosystem
- 5 Functions of Ecosystem
- 6 Conclusion
What Is the Meaning of Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other. If you’ve ever seen a video or pictures of a coral reef or rainforest, you would see that it’s one example of an ecosystem. The word ”Ecosystem” can be used to mean a local environment (such as your backyard) or the whole earth itself, which is called a “Global Ecosystem”
Now we will understand the meaning and definition of every ecosystem on the earth.
What Is a Terrestrial Ecosystem?
Ecosystems are varied and are found everywhere on the planet. Ecosystems are further divided based on the places they are found. Likewise, all the ecosystems that have evolved on the Earth’s surface or land are called terrestrial Ecosystems. In other words, the terrestrial Ecosystem is the community of living organisms residing on the ground. The terrestrial Ecosystem is divided into the forest, grassland, tundra, desert, mountain, and savanna ecosystem.

What Is a Forest Ecosystem?
On land, the forest ecosystem is the largest and is characterized by a large number of trees in a particular area. Therefore, trees are the most dominating characteristic of the forest ecosystem. Forest ecosystems are full of diversity, and thousands of species of plants, animals, insects, and birds call it their home.
Today, about 30% of Earth’s landmass is covered in forest. Depending on the trees, forests are classified into coniferous, deciduous, and mixed forests. Also, forests are classified depending upon the vegetation zone – Tropical rainforest, Temperate rainforest, Deciduous and mixed forest. Forest ecosystems can also be divided into five parts – tree layer, shrub layer, herb layer, moss layer, and root layer.

What Is a Grassland Ecosystem?
A grassland ecosystem is a terrestrial ecosystem covered with grass and not trees. The dry climatic conditions in the grassland prevent the growth of trees.
According to the expert, around 25% of Earth’s surface is covered by grassland. In general, grassland arises in those areas that receive little rainfall. Depending upon specific characteristics, grassland can be classified as steppes, pampas, savannahs, or prairies. Although the grassland remains dry and there are very few trees, it is still a thriving ecosystem. Several small and large animal species live in grassland, making it a diverse ecosystem.
What Is a Tundra Ecosystem?
Tundra is a type of Ecosystem characterized by a freezing climate, frozen subsoil, and few or no trees. It’s generally flat land with the ground covered with lichens and mosses. Tundra is mainly located in the polar region – it means a harsh cold climate with a long winter. Only a few plants and animals adapted to these conditions can survive in the tundra ecosystem.
Most of the Tundra extends across Alaska, northern Canada, Siberia, southern Greenland, and the European Arctic coast. While in the southern hemisphere, tundra is found in the extreme south of Argentina and Chile, Antarctica, and subantarctic islands. Polar bears, arctic foxes, wolves, arctic hares, and Siberian lemmings live in the tundra ecosystem.

What Is a Desert Ecosystem?
A desert ecosystem is an area on land with little to no trees, herbs, and shrubs and receives extremely low rainfall throughout the year. Depending on the region, deserts can be very hot or very cold. These are classified as dry and hot deserts (Sahara) or cold and ice deserts ( Antarctica).
According to experts, deserts cover around a fifth of all land surface. Deserts can further be divided, depending upon the soil type – sandy deserts, gravel deserts, stone deserts, and salt flats. Due to extreme climatic conditions, only a few plant and animal species are found in the desert ecosystem. These include, for example, snakes, scorpions, gazelles, or camels.
What Is a Mountain Ecosystem?
The mountain ecosystems are characterized by high relief on the Earth’s surface. Mountains are high-rise landscapes with varied climatic conditions, flora, and fauna. On the lower slopes, mountains are generally dominated by forests. However, as you go up, the temperature keeps on falling, and at the top, there is significantly less or no vegetation. The top of the mountain is usually covered with snow.
Despite the harsh conditions, mountains are full of different plants and animal species. Animals and birds residing in the mountains have evolved certain traits to survive on higher altitudes. Brown Bear, Yak, Himalayan Tahr, Lammergeier, Alpine Chough, etc., are found in the mountain ecosystem.
What Is a Savanna Ecosystem?
Savanna is a type of grassland ecosystem found on either side of the equator bordering rainforest. The climate in the savanna ecosystem alternates between dry and rainy seasons; however, the temperature consistently remains high. Overall, the Savannah ecosystem can be characterized as a hot, grassy landscape with very few scattered trees.
There are mainly three types of Savanna – wet, dry, and thornbush savannah. Animal species differ depending on the types and the continent they are found in. In general, you will find Armadillos, tapirs, jaguars, maned wolves, etc., in the Savannah ecosystem.
What Is an Aquatic Ecosystem?
Life not only thrives on land but is also as prevalent in the water. An aquatic ecosystem consists of plants, animals, and other organisms that live in water.

The aquatic system can be both freshwaters as well as saltwater. Similarly, it can also be still water like a lake or pond ecosystem, running water like rivers, and salty water like seas and oceans. All lifeforms that live in water constitute an aquatic ecosystem.
It’s the largest Ecosystem and covers about 70% of Earth’s surface. Aquatic lifeforms have evolved traits that allow them to thrive in an aquatic Ecosystem. Moreover, the aquatic ecosystem is further divided into the marine and freshwater ecosystems.
What Is a Freshwater Ecosystem?

Freshwater ecosystem systems are those water bodies that do not contain salt. Lakes, ponds, and rivers are all examples of freshwater ecosystems. Species found in the freshwater ecosystem have adapted to the less saline conditions and usually won’t survive in the marine ecosystem. Many amphibians, fish, and aquatic plants are found in the freshwater ecosystem.
What Is a Marine Ecosystem?

Unlike the freshwater Ecosystem, the marine ecosystem is extremely saline. The presence of salt in high concentrations is the primary characteristic of the marine ecosystem. Seas and oceans are perfect examples of marine ecosystems. Contrary to the freshwater ecosystem, the marine Ecosystem is quite extensive and covers nearly all of the globe. Similarly, the diversity of flora and fauna is quite extensive too. It’s the ocean where life originated, and the ecosystem is so vast that we still haven’t classified each and every plant and animal species that live out there.
What Is a Community in An Ecosystem?
A community in an ecosystem is defined as the set of mutually interacting populations of species living in a specific area. In some cases, the community can also refer to the dominant population of certain species in a given area.
Take, for example, the salamander community living near a mountain stream. Moreover, a community can also refer to the place where species thrive, like a desert community, forest community, or pond community. Furthermore, communities also have traits, just like any living organism. These are generally classified as diversity, relative abundance, and stability.
What Are the Structural Components of The Ecosystem?
The Ecosystem is a complex mix of organisms interacting with each other as well as the environment. Moreover, the Ecosystem has a defined structure that maintains the flow of energy throughout the system and keeps it running.
The structural components or structural aspects of the ecosystem include the biotic (living) and abiotic (physical features).

In simple words, the structural components of the Ecosystem define the interactions going on between the living and non-living components of the system.
Structure of Forest Ecosystem
The forest ecosystem is characterized by a thick cover of large trees and the animals that reside there. Like any ecosystem, the forest also comprised biotic and abiotic structural components. Trees, animals, plants, moss, insects, birds, etc., constitute the biotic component of forest ecosystems, while the air, soil, moisture, etc., comprise the abiotic structural components of the forest ecosystem.
Structure of Aquatic Ecosystem
Similar to the terrestrial Ecosystem, the aquatic system also includes a structure. The characteristics of ecosystems remain the same underwater too. Both abiotic and biotic factors come together to make life thrive in the aquatic system too. Water, salinity, depth, temperature, nutrients, etc., constitute the abiotic components in the aquatic system. In contrast, all the living organisms residing in that aquatic system form the biotic component of the aquatic Ecosystem.
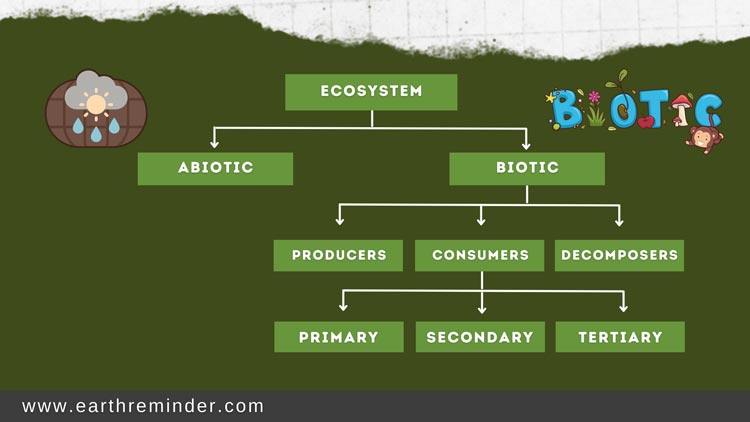
Functional Components of The Ecosystem
The ecosystem acts as a unit, where each component plays its part in keeping the ecosystem functioning and life thriving. Similar to structural components, the ecosystem also has functional components. These are Productivity, Decomposition, Energy Flow, Nutrients Cycling, and Trophic level. Functional aspects of ecosystem are given below;
- Productivity: Productivity is defined as the amount of biomass available and the rate at which the living components produce the biomass. It can further be divided into primary productivity and secondary activity. Primary activity denotes the biomass produced by producers via the help of sunlight, while secondary productivity depicts the amount of biomass produced by consumers.
- Decomposition: Decomposition denotes the breaking of biomass into simpler compounds by decomposers. This way, the dead mass is returned to the system and again employed to continue the lifecycle in the Ecosystem.
- Energy Flow: Energy Flow denotes the flow of energy from the highest to the lowest level in the Ecosystem and nurtures the whole system. At the top level are the producers, which directly take in sunlight to continue their bio-functions. From producers, the energy flows to the consumer who feeds on producers, and the energy flow continues its journey to lower levels.
- Nutrient-Cycle: All the nutrients that nurture the ecosystem remain in that system and continue recycling to keep the system well-fed and running. This continuous recycling and utilization of nutrients is known as the nutrient cycle.
- Trophic Level: The ecosystem is a closely linked system, and each organism plays its part in keeping it going. Depending upon how an organism meets its nutrients needs, it occupies different levels in an ecosystem. Likewise, producers are at the top, then come consumers, and lastly, decomposers.
Functions of Ecosystem
The function of the Ecosystem comprises the collective actions of plants, animals, microbes, etc., and the impact of those actions on the ecosystem as a whole. Some of the functions of the Ecosystem directly benefit humans too, and are known as ecosystem services.
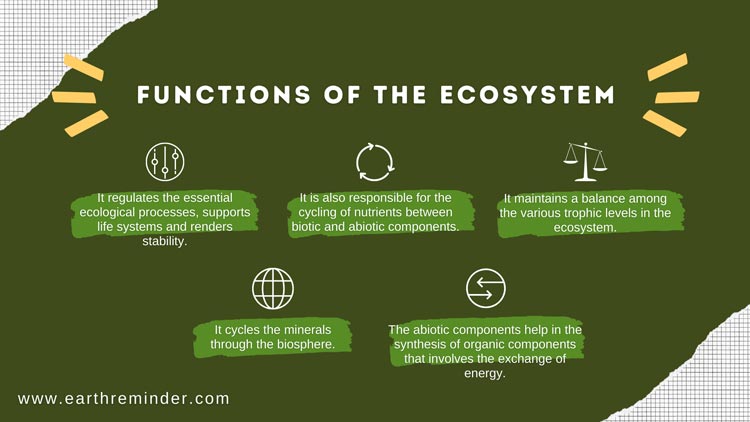
Examples of ecosystem functions are biomass production, storage, filtration of water, soil formation, etc. Here are some more examples;
- The ecosystem provides the conditions and necessary components for life to thrive.
- It provides the habitat for living organisms to live and reproduce.
- The ecosystem powers the nutrients cycle and keeps the transitions going on between living and non-living components.
- It maintains the energy flow from the top level to the bottom of the food chain and nourishes all organisms occupying different trophic levels.
The Function of The Forest Ecosystem
Forests are the major source of woods and several medicinal plants. Besides being home to countless species of plants and animals, the Terrestrial ecosystem also prevents soil erosion, checks water flow, stores excess water, and replenishes groundwater. Additionally, forests also regulate the water and oxygen cycle and limit the amount of carbon-di-oxide in the atmosphere.
The Function of The Grassland Ecosystem
Grasslands may not be covered with a thick green cover; still, they perform several vital functions. Large open grass-covered landscapes provide ample fodder for livestock. Additionally, grassland also provides a habitat and breeding ground for several species. Also, grassland prevents soil erosion and contributes to water conservation.
The Function of The Desert Ecosystem
Despite being dry, the desert still provides habitat to a variety of specially adapted plants and animals. Extreme weather conditions may not allow large settlements; however, deserts are a rich source of essential minerals that are economically valuable. Moreover, the harsh conditions further promote the concentration of minerals which provide easy access, high quality, and large quantities.
Aquatic Ecosystem Functions
Aquatic ecosystems are home to millions of aquatic species ranging from fish to crabs, corals, etc. Besides, the aquatic Ecosystem replenishes the groundwater, continues the flow of water, and provides fresh water for consumption.
The Function of The Marine Ecosystem
Although oceans are highly saline and not fit for drinking, the marine ecosystem provides habitat to the largest number of aquatic plants and animals. It’s the largest ecosystem on the planet and regulates the water cycle and rainfall throughout the globe. Also, oceans absorb the largest amount of carbon-di-oxide and prevent imbalance in the atmosphere. Moreover, the marine ecosystem regulates the oxygen cycle too. A large part of oxygen in the atmosphere comes directly from the ocean.
Conclusion
Ecosystems are complex systems that provide a variety of functions and services. They are composed of different components, each with its own specific role to play. The structure of an ecosystem determines how it functions, and how resilient it is to change. Ecosystems can be found in all corners of the world, from forests to deserts, mountains to oceans, and they perform vital roles in supporting life on Earth.
If you like this article, please comment below for any queries. Also, share it with your friends and family members.